CSS3 Viewport units vh, vw, vmin and vmax explained
Sometimes we need to fit our webpage content into viewport (visible browser window). Some developers achieve this using Javascript by checking the size of viewport and then they resize the content accordingly to fit it in the viewport. When user resizes the browser window, the script runs again and resizes the elements on the page.
But we can achieve the same using CSS with vh, vw, vmin and vmax.
One unit of any of the 4 terms is 1% of the viewport axis:
1vw = 1% of the viewport width 1vh = 1% of the viewport height 1vmin = 1vw or 1vh, whichever is smaller 1vmax = 1vw or 1vh, whichever is larger
For Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
font-size: 5.9vw;
}
h2{
font-size: 3.0vh;
}
p{
font-size: 2vmin;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<h2>Hello</h2>
<p>I am a software developer.</p>
</body>
</html>
Upon running this code you will get output like this:
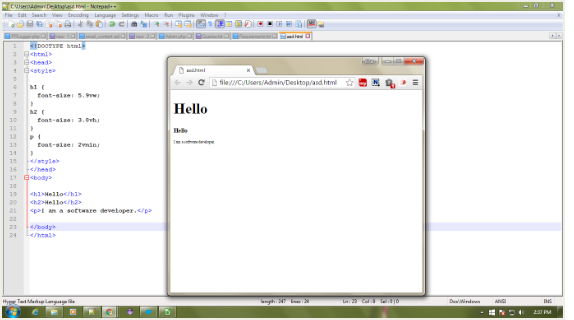
Just resize the window and see the magic. The elements will resize accordingly to the size of screen.
