If you run a set of commands on regular basis you can use Ubuntu ‘alias’ command to create an alias for entire set and use the alias name in future. For example these are a set of commands to compile a project and copy resulting .war file it to a different location:
cd ~/myproject/
mvn -DskipTests clean install
cp ~/myproject/target/myfile.war /opt/apache-tomcat-7.0.55/webapps/
Basic Syntax of alias command: alias [-p] [Name=”value”]
Alias: name of the command
p: To show list of aliases
Name: the name you want to give to your command which you want to use using an alias.
value: Type you complete command here.
To separate commands, use the && symbol.
In above example, we can do like this:
alias compile_myproj = ‘cd ~/myproject/ && mvn -DskipTests clean install
&& cp ~/myproject/target/myfile.war /opt/apache-tomcat-7.0.55/webapps/’
Now you can run compile_myproj command in future to execute all 3 commands in sequence.
To permanently make compile_myproj available when you reboot the machine, Open your .bashrc file inside your home folder you will see following lines of code at the bottom of the file:
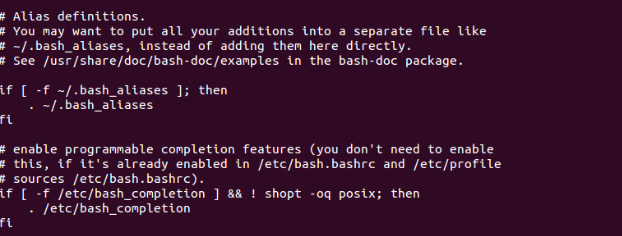
Steps:
1. Create .bash_aliases file inside your home folder.
2. Add your alias there. In our case we have added following command inside .bash_aliases file:
alias compile_myproj = ‘cd ~/myproject/ && mvn -DskipTests clean install
&& cp ~/myproject/target/myfile.war /opt/apache-tomcat-7.0.55/webapps/’
3. Then run source ~/.bashrc command to refresh .bashrc file (you do not need to do this when you reboot your machine).
