Artificial Intelligence
AI is a technique that tries to enable machines to copy human behavior. It is the study of the development of computer systems so they are able to perform tasks normally done by the human mind, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making and translating different languages.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or software that thinks smartly, in a similar way as humans think.
AI is accomplished by studying how the human brain thinks, and how humans learn, decide, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the results of this study it develops intelligent software and systems.

A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a buzzword today, although this term is not new. A group of avant-garde experts from different backgrounds decided to organize a summer research project on AI in 1956. Four intelligent brains started the research project; John McCarthy (Dartmouth College), Marvin Minsky (Harvard University), Nathaniel Rochester (IBM), and Claude Shannon (Bell Telephone Laboratories).
The main purpose of this project was to challenge “every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence that can in principle be so precisely described, that a machine can be made to adhere to it”.
The proposal of the summits included:
- Automatic Computers
- How Can a Computer Be Technically Programmed to Use a Language?
- Neuron Nets
- Self-improvement
It led to the idea that smart/automate/intelligent computers can be made. Then a new generation began, full of hope – Artificial intelligence.
Type of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can be divided into three subfields:
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Deep learning
Machine Learning
Machine learning is the art of studying algorithms that learn from examples and experiences. It is based on the idea that there exist some patterns in the data that were identified and used for future predictions. The difference from hardcoding rules is that the machine learns on its own to find such rules.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning. Deep learning does not mean the machine learns more in-depth knowledge; it means the machine uses different layers to learn from the data. The depth of the model is represented by the number of layers in the model. Google LeNet model counts 22 layers for image recognition.
In deep learning, the neural network is the learning phase. A neural network is the type of architecture where the layers are placed like stack on top of each other.
AI vs. Machine Learning
Our daily life devices like smartphones, smart led bulbs, automatic doors, etc or even the internet use Artificial intelligence. Very often, AI and machine learning are used interchangeably by many companies that want to announce their latest innovation. However, Machine learning and AI are not one thing, they are different in some ways.
How To Get Into AI:
Before getting into Artificial Intelligence, you must have at least basic fundamental knowledge of the following so that you can understand the concepts easily:
- Computer languages like C, C++, Java, Python, etc.
- Algorithms
- Knowledge of essential Mathematics such as derivatives, probability theory, statistics, etc.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
There are various applications of Artificial Intelligence in the Industry, here are a few of the important ones that are present in our day to day tasks.
- Speech Recognition
- Machine Translation
- Facial Recognition and Automatic Tagging
- Virtual Personal Assistants
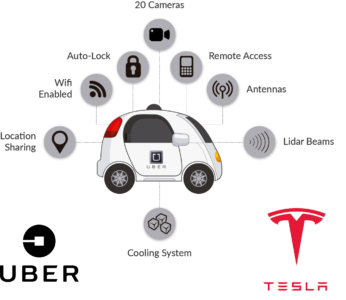
- Self Driving Car
- Chatbots


Programming Without and With AI
The programming without and with AI is different in the following ways −
| Programming Without AI | Programming With AI |
|---|---|
| A computer program without AI will solve only those problems or situations for which it is developed | A computer program with AI can answer the generic questions and also analyze some problems and react according to that. |
| Modification in the software programs can lead to change in its architecture/structure. | AI programs can adhere to new modifications by adding highly independent pieces of information or data together. Hence you can modify even a very small piece of information of program without affecting its original structure. |
| Modification is not fast and easy. It may lead to affecting the whole program adversely. | Very fast and easy program modification after embedding AI |
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Following are some main advantages of Artificial Intelligence:
- Fewer errors and High Accuracy: AI devices or systems are prone to fewer errors and high accuracy as they take decisions as per previous analysis pre-experience or information.
- High-Speed systems: AI systems can be made to work with very high-speed and fast-decision making.
- High-reliability systems: They are highly reliable and can perform the same action multiple times with high accuracy without any human effort.
- Useful in Dangerous Situations: AI machines can be helpful in situations like bomb defusing, ocean floor exploration, where employing a human being can be risky.
- Digital Assistant: AI can be very useful to provide digital assistance to users like chatbots used by various E-commerce websites.
- Useful as a public utility: AI can be very useful for public utilities such as a self-driving car which can make our journey safe without getting tired and hassle-free.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Every automated technology has some disadvantages, and the same goes for Artificial intelligence. Being so advantageous technology, it still has some drawbacks which we need to keep in our mind while creating an AI system. Following are the disadvantages of AI:
- High Cost: The hardware and software cost of AI is very high as it requires lots of maintenance to meet current world requirements.
- Can’t think extraordinary: Even we are making smarter machines with AI, but still, they cannot work out of the box as they do not have brains like humans, as the robot machines will only do that work for which they have been trained, or programmed.
- No feelings/emotions: AI machines can be an outstanding performer in technology, but still they lack the feeling like humans so they cannot make any kind of emotional attachment with humans, and may sometime be harmful to humans if the proper care is not taken.
- Laziness in humans: With the increment of technology, people are getting more dependent on devices, machines that do their work in just a few seconds. As a result, they are losing their mental capabilities and physical health.
- No real creativity: As humans are creative and can imagine some new ideas with the brain but AI machines cannot beat this power of human intelligence and cannot be creative and imaginative.
Agent In AI
An agent can be anything that perceives its environment through sensors and act upon that environment through actuators. An Agent runs in the cycle of perceiving, thinking, and acting. An agent can be:
- Human-Agent: A human agent has eyes, ears, and other organs that work for sensors and hand, legs, vocal tract work for actuators.
- Robotic Agent: A robotic agent can have an infrared range finder, NLP for sensors, cameras and different kinds of motors for actuators.
- Software Agent: Software agents can have keystrokes, file contents as sensory input and act on those inputs and display output on the screen.
Hence the world around us is full of agents such as thermostat, cellphone, camera, and even we are also agents. Before moving forward, we should first know about sensors, effectors, and actuators.
Sensor: Sensor is a device that detects the change in the environment and sends the information to other electronic devices. An agent observes its environment through sensors.
Actuators: Actuators are the components of machines that convert energy into motion. The actuators are only responsible for moving and controlling a system. An actuator can be an electric motor, gears, rails, etc.
Effectors: Effectors are devices that affect the environment. Effectors can be legs, wheels, arms, fingers, wings, fins, and display screen.
Careers In AI
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Data Scientist
- Business Intelligence Developer
- Research Scientist
- Big Data Engineer/Architect
