Suppose we have two tables : articles and article_comments
CREATE TABLE articles( `id` INT( 11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , `title` VARCHAR( 200 ) NOT NULL , `content` VARCHAR( 500 ) NOT NULL , `author_name` VARCHAR( 20 ) DEFAULT 1 NOT NULL , `author_email` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL , `created_date` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `last_modified_time` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE NOW( ) , PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ) ) ENGINE = INNODB;
CREATE TABLE article_comments( `id` INT( 11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , `article_id` INT( 11 ) NOT NULL , `author_comments` VARCHAR( 200 ) , `user_name` VARCHAR( 30 ) , `user_email` VARCHAR( 50 ) , `user_comments` VARCHAR( 200 ) , `created_date` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ) , CONSTRAINT `fk_articles` FOREIGN KEY ( `article_id` ) REFERENCES `articles` ( `id` ) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE ) ENGINE = INNODB;
In first table, let we have records:
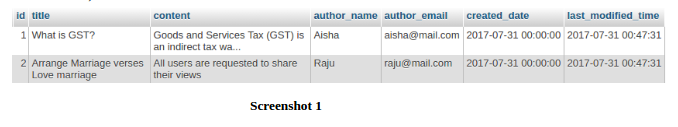
In second table, let we have records:
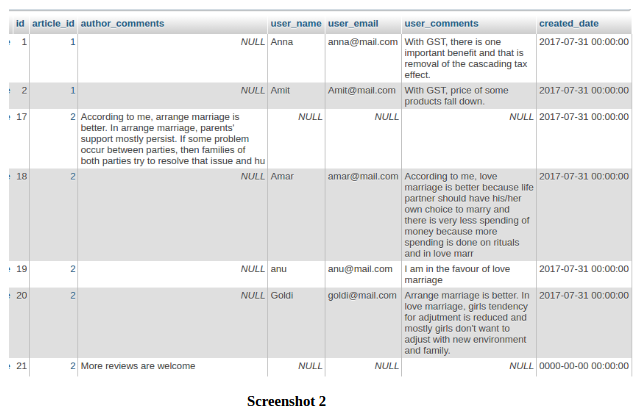
From screenshot 2, it can be observed that, at a time, either author comment is stored or user comment is stored. In this table, article_id is foreign key to articles table. Author_comments column stores comments provided by author of article and user_comments column stores comments provided by any user/public/person worldwide.
Now, suppose we want to fetch records in following form:
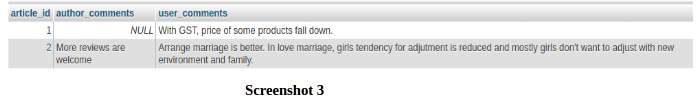
From screenshot 3, we can see that latest user_comments and author_comments are displaying in single row per article_id. If any of user_comments or author_comments does not exist, then NULL will be displayed. Latest user comments and author comments per article basis, have been fetched in single row, with the following query:
SELECT t.article_id, MAX( t.author_comments ) AS author_comments, MAX( t.user_comments ) AS user_comments FROM ( SELECT article_id, MAX( CASE WHEN author_comments IS NOT NULL THEN id END ) AS author_comment_id, MAX( CASE WHEN user_comments IS NOT NULL THEN id END ) AS user_comment_id FROM article_comments GROUP BY article_id ) AS x JOIN article_comments AS t ON t.id IN ( author_comment_id, user_comment_id ) GROUP BY article_id;
Now, suppose we also want to show author name, title from articles table along with data shown in screenshot 3, then this can be implemented with following query:
SELECT title, author_name, author_comments, user_comments FROM articles LEFT JOIN ( SELECT t.article_id, MAX( t.author_comments ) AS author_comments, MAX( t.user_comments ) AS user_comments FROM ( SELECT article_id, MAX( CASE WHEN author_comments IS NOT NULL THEN id END ) AS author_comment_id, MAX( CASE WHEN user_comments IS NOT NULL THEN id END ) AS user_comment_id FROM article_comments GROUP BY article_id ) AS x JOIN article_comments AS t ON t.id IN ( author_comment_id, user_comment_id ) GROUP BY article_id ) AS comments_table ON comments_table.article_id = articles.id;
And finally, we have output as shown below with above query:
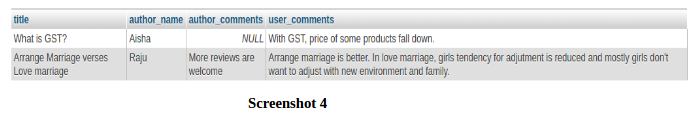
According to requirements, we can display other fields also like author_email or user_name or user_email etc.
